ポリフェノール性抗酸化物質による活性酸素消去に関する研究は、古く1800年代から現在に至るまで展開されています。近年は特に癌や生活習慣病の原因化学種として活性酸素種(Reactive Oxygen Species :ROS)が挙げられ、ROS消去メカニズムの解析が進んでいます。
近年の研究では、Dismutation(SOD、不均化反応)、還元的一電子移動(SET)、水素原子移動(HAT)といった、旧来より考えられていたROS消去メカニズムとは別に、プロトン電子共役移動反応(Proton-coupled electron transfer : PCET反応)が提唱され、その関連研究が盛んにおこなわれています。
当研究室では、PCETの中でも特に、協奏的プロトン電子共役移動反応(Concerted PCET)が多くのポリフェノール類ROS消去メカニズムの実態であることを詳細に解析してきました。
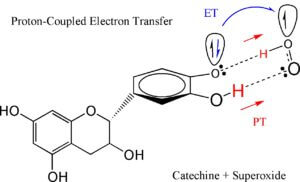
この反応機構では、抗酸化ポリフェノールの一つであるカテキンやクエルセチン等のフラボノイド類が、分子構造の一部であるカテコール骨格とSuperoxideとの間の水素結合を介して、水酸基プロトンと電子を協奏的(concerted)に移動させることで、効率的に活性酸素種を消去できます。
この際(Fig.1)、水素結合(O-H-O)のσ軌道上を直線的に移動するプロトンに対して、電子はπ軌道上を移動します。
特に2プロトンと1電子がカテコール骨格からSuperoxideへ協奏的に移動する様子をconcerted 2PCET機構と名付け、抗酸化メカニズムの中核を成す効率的な反応であると考えられます。
過去の関連文献
- Electrochemical and Mechanistic Study of Reactivities of α-, β-, γ-, and δ-Tocopherol toward Electrogenerated Superoxide in N,N-Dimethylformamide through Proton-Coupled Electron Transfer
- Tatsushi Nakayama, Ryo Honda, Kazuo Kuwata, Shigeyuki Usui and Bunji Uno
- Antioxidants 2022, 11(1), 9
- DOI: doi.org/10.3390/antiox11010009
- Reactivities of Hydroxycinnamic Acid Derivatives Involving Caffeic Acid toward Electrogenerated Superoxide in N,N-Dimethylformamide
- Tatsushi Nakayama, Bunji Uno
- Electrochem, 2022, 3(3), 347-360
- DOI: doi.org/10.3390/electrochem3030024
- Electrochemical and Mechanistic Study of Superoxide Scavenging by Pyrogallol in N,N-Dimethylformamide through Proton-Coupled Electron Transfer
- Tatsushi Nakayama, Ryo Honda, Kazuo Kuwata, Shigeyuki Usui, Bunji Uno
- Electrochem, 2022, 3, 1, 115-128
- DOI: doi.org/10.3390/electrochem3010008
- Concerted two-proton–coupled electron transfer from catechols to superoxide via hydrogen bonds
- Electrochem. Acta, 2016, 208, 1, 304-309
- Tatsushi Nakayama, Bunji Uno (中山辰史、宇野文二)
- https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.05.034
- Importance of Proton-Coupled Electron Transfer from Natural Phenolic Compounds in Superoxide Scavenging
- Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 63, 12, 967-973
- Tatsushi Nakayama, Bunji Uno (中山辰史、宇野文二)
- https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.c15-00447
- Structural Properties of 4-Substituted Phenols Capable of Proton-Coupled Electron Transfer to Superoxide
- Int. J. Adv. Res. Chem. Sci. 2016, 3, 1, 11-19
- Tatsushi Nakayama, Bunji Uno (中山辰史、宇野文二)
- http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2349-0403.0301002
- Quinone–Hydroquinone π-Conjugated Redox Reaction Involving Proton-coupled Electron Transfer Plays an Important Role in Scavenging Superoxide by Polyphenolic Antioxidants
- Chem. Lett. 2010, 39, 3, 162-164
- Tatsushi Nakayama, Bunji Uno (中山辰史、宇野文二)
- https://doi.org/10.1246/cl.2010.162
お問合わせ
内容に関するお問い合わせ、共同研究の依頼、講演依頼、その他、ご質問はこちらより。